
While research and experimentation with blockchain technology across sectors has been underway for several years, few organizations have deployed it. Although central banks are among the most cautious and prudent institutions in the world, a new white paper published by the World Economic Forum indicates that these institutions, perhaps surprisingly, are among the first to implement blockchain technology.
虽然跨部门的区块链技术的研究和实验已经进行了几年,但是很少有组织部署它。尽管各国央行是世界上最谨慎、最谨慎的机构之一,但世界经济论坛(world Economic Forum)发表的一份最新白皮书显示,这些机构或许出人意料地率先实施了区块链技术。
Central bank activities with blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) are not always well known or communicated. As a result, there is a lot of speculation and misunderstanding. Yet dozens of central banks around the world – from Sweden to South Africa to Singapore – are actively investigating whether blockchain can help solve long-standing issues in banking, such as payment-system efficiency, payment security and resilience, as well as financial inclusion.
央行使用区块链和分布式分类帐技术(DLT)进行的活动并不总是众所周知或相互沟通的。因此,有很多猜测和误解。然而,从瑞典到南非,再到新加坡,全球数十家央行都在积极调查区块链能否帮助解决银行业长期存在的问题,比如支付系统效率、支付安全和弹性,以及金融包容性。
These organizations, tasked with overseeing a nation’s monetary policy and financial and economic stability, are very cautious to implement any technology or solution that can have adverse consequences. Yet many central banks are actively researching a variety of use cases to explore the technology’s potential in controlled, secure settings.
这些组织的任务是监督一个国家的货币政策、金融和经济稳定,它们非常谨慎地执行任何可能产生不利后果的技术或解决方案。然而,许多央行正在积极研究各种用例,以探索该技术在受控、安全设置中的潜力。
Top 10 central bank use cases
央行的十大用例
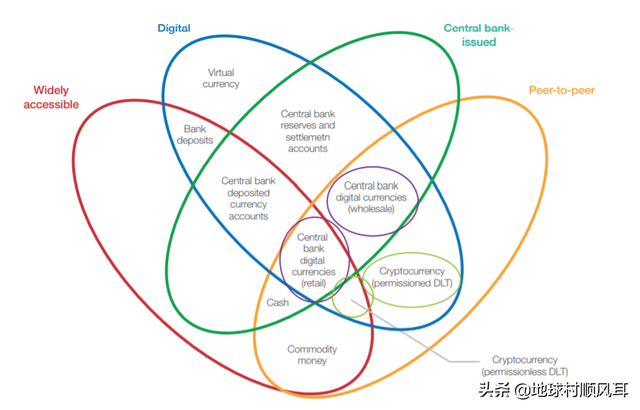
1. Retail central bank digital currency (CBDC) – A central bank-issued digital currency that is operated and settled in a peer-to-peer and decentralized manner (with no intermediary) and is widely available for consumer use. This form of CBDC serves as a complement or substitute for physical cash and an alternative to traditional bank deposits. Central banks from several countries are experimenting with this, including those from the eastern Caribbean, Sweden, Uruguay, the Bahamas and Cambodia.
1. 零售中央银行数字货币(CBDC) -中央银行发行的数字货币,以点对点和分散的方式(没有中介)运行和结算,广泛供消费者使用。这种形式的CBDC作为实物现金的补充或替代品,是传统银行存款的替代品。一些国家的央行正在尝试这种做法,包括东加勒比、瑞典、乌拉圭、巴哈马和柬埔寨的央行。
2. Wholesale CBDC – A central bank-issued digital currency that is operated and settled in a peer-to-peer and decentralized manner (with no intermediary) but is only available only for commercial banks and clearing houses for use in the wholesale interbank market. Central banks researching this include those from South Africa, Canada, Japan, Thailand, Saudi Arabia, Singapore and Cambodia.
2. 批发CBDC——中央银行发行的一种数字货币,以点对点和分散的方式运行和结算(没有中间机构),但仅供商业银行和清算机构在批发银行间市场使用。研究这一问题的央行包括来自南非、加拿大、日本、泰国、沙特阿拉伯、新加坡和柬埔寨的央行。
3. Interbank securities settlement – A focused application of blockchain-based digital currency, including CBDC, enabling the rapid interbank clearing and settlement of securities for cash. The goal is to develop “delivery versus payment” interbank systems where two parties trading an asset, such as a security for cash, can conduct the payment for and delivery of the asset simultaneously. Central banks exploring this option include the Bank of Japan, Monetary Authority of Singapore, Bank of England and Bank of Canada.
3.银行间证券结算-专注于基于区块链的数字货币的应用,包括CBDC,使银行间证券的现金快速清算和结算。其目标是开发“交付与支付”银行间系统,在该系统中,交易一项资产(如现金担保)的双方可以同时进行该资产的支付和交付。正在探索这一选项的央行包括日本央行(Bank of Japan)、新加坡金融管理局(Monetary Authority of Singapore)、英国央行(Bank of England)和加拿大央行(Bank of Canada)。
4. Payment system resiliency and contingency – The use of DLT in a primary or backup domestic interbank payment and settlement system to provide safety and continuity from threats, including technical or network failure, natural disaster, cybercrime and other threats. Often, this use case is coupled with others as part of the set of benefits that a DLT implementation could potentially offer. The central banks researching this use case include the Central Bank of Brazil and the Eastern Caribbean Central Bank.
4. 支付系统的弹性和偶然性-在国内银行间支付和结算系统的主要或备份中使用DLT,以提供安全性和连续性,免受威胁,包括技术或网络故障、自然灾害、网络犯罪和其他威胁。通常,这个用例与其他用例结合在一起,作为DLT实现可能提供的一系列好处的一部分。研究这个用例的中央银行包括巴西中央银行和东加勒比中央银行。
5. Bond issuance and lifecycle management – The use of DLT in the bond auction, issuance or other lifecycle processes to reduce costs and increase efficiency. This concept could be applied to bonds issued and managed by sovereign states, international organizations or government agencies. Central banks or government regulators could be “observer nodes” to monitor activity where relevant. The World Bank launched the first blockchain-based bond, called the “bond-i”, in August 2018.
5. 债券发行和生命周期管理-在债券拍卖、发行或其他生命周期过程中使用DLT,以降低成本和提高效率。这一概念可适用于主权国家、国际组织或政府机构发行和管理的债券。央行或政府监管机构可以成为“观察节点”,在相关领域监控活动。2018年8月,世界银行发行了第一种区块链债券,名为“邦德-i”。
6. Know your customer (KYC) and anti-money-laundering (AML) – Digital KYC/AML processes that leverage DLT to track and share relevant customer payment and identity information to streamline processes. This solution could connect to a digital national identity platform or plug into pre-existing e-KYC or AML systems. It also could potentially interact with CBDC as part of payments and financial activity tracking. Central banks exploring it include the Hong Kong Monetary Authority.
6. 了解您的客户(KYC)和反洗钱(AML)-利用DLT跟踪和共享相关客户支付和身份信息以简化流程的数字KYC/AML流程。该解决方案可以连接到数字国家身份平台,或插入现有的e-KYC或AML系统。它还可能与CBDC互动,作为支付和金融活动跟踪的一部分。正在探讨这一问题的央行包括香港金融管理局(Hong Kong Monetary Authority)。
7. Information exchange and data-sharing – The use of distributed or decentralized databases to create alternative systems for information and data sharing between or within related government or private sector institutions. Among others, the Central Bank of Brazil is researching this use case.
7. 信息交换和数据共享-使用分布式或分散的数据库,为相关政府或私营部门机构之间或内部的信息和数据共享创建替代系统。巴西央行正在研究这个用例。
8. Trade finance – The employment of a decentralized database and functionality to enable faster, more efficient and more inclusive trade financing. This improves on today’s trade finance processes which are often paper-based, and labour- and time-intensive. Customer information and transaction histories are shared between participants in the decentralized database, while maintaining privacy and confidentiality where needed. Central banks researching this include the Hong Kong Monetary Authority.
8. 贸易融资-使用分散的数据库和功能,使贸易融资更快、更有效和更具包容性。这改善了目前的贸易融资流程,这些流程通常以纸张为基础,劳动和时间密集。在分散的数据库中,客户信息和事务历史在参与者之间共享,同时在需要时维护隐私和机密性。研究这一问题的央行包括香港金融管理局(Hong Kong Monetary Authority)。
9. Cash money supply chain – The use of DLT for issuing, tracking and managing the delivery and movement of cash from production facilities to the central bank and commercial bank branches. This could include the ordering, depositing or movement of funds, and could simplify regulatory reporting. Central banks exploring include the Eastern Caribbean Central Bank.
9. 现金货币供应链-使用DLT发行、跟踪和管理从生产设施到中央银行和商业银行分支机构的现金交付和流动。这可能包括资金的订购、存放或转移,并可能简化监管报告。正在探索的央行包括东加勒比央行(Eastern Caribbean Central Bank)。
10. Customer SEPA Creditor Identifier (SCI) provisioning – A blockchain-based decentralized sharing repository for Single Euro Payment Area (SEPA) credit identifiers, managed by the central bank and commercial banks in the SEPA debiting scheme, could offer a faster, more streamlined, decentralized system for identity provisioning and sharing. It could replace pre-existing manual and centralized processes that are time- and resource-intensive. This has already been implemented in the Bank of France’s Madre project.
10. 客户SEPA债权人标识符(SCI)供应-一个基于区块链的分散共享存储库,用于单一欧元支付区(SEPA)信用标识符,由中央银行和商业银行在SEPA借方计划中管理,可以提供一个更快、更精简、分散的身份供应和共享系统。它可以替代现有的手工和集中式流程,这些流程需要大量的时间和资源。这已经在法国银行的Madre项目中实施。
For each of these use cases (listed in order of popularity), there is at least one central bank actively researching this area. This research and experience vary across countries, and many central bank researchers have yet to conclude whether DLT can provide value to their processes given salient risks and limitations.
对于这些用例中的每一个(按流行程度列出),至少有一个中央银行在积极地研究这个领域。各国的研究和经验不尽相同,许多央行研究人员尚未得出结论,考虑到明显的风险和局限性,DLT是否能够为他们的过程提供价值。
In rare cases, such as with the Bank of France, a central bank has successfully deployed a DLT-based application. In other cases, central banks have concluded that blockchain technology does not provide valuable opportunities for their economies when considering the risks and downsides. At the very least, many are monitoring developments among peer institutions and within the private cryptocurrency markets.
在极少数情况下,比如法国央行,央行已经成功地部署了一个基于dll的应用程序。在其他情况下,各国央行已经得出结论,在考虑风险和不利因素时,区块链技术并没有为它们的经济提供宝贵的机会。至少,许多机构正在监控同行机构之间以及私人加密货币市场内部的事态发展。
Over the next four years, we should expect to see many central banks decide whether they will use blockchain and DLT to improve their processes and economic welfare. Given the systemic importance of central bank processes, and the relative immaturity of blockchain technology, the banks must carefully consider all known and unknown risks to implementation.
在未来四年,我们应该会看到,许多央行将决定是否使用区块链和DLT来改善它们的流程和经济福利。鉴于央行流程的系统性重要性,以及区块链技术相对不成熟,银行必须认真考虑实施过程中所有已知和未知的风险。
来源:FINTECH RANKING